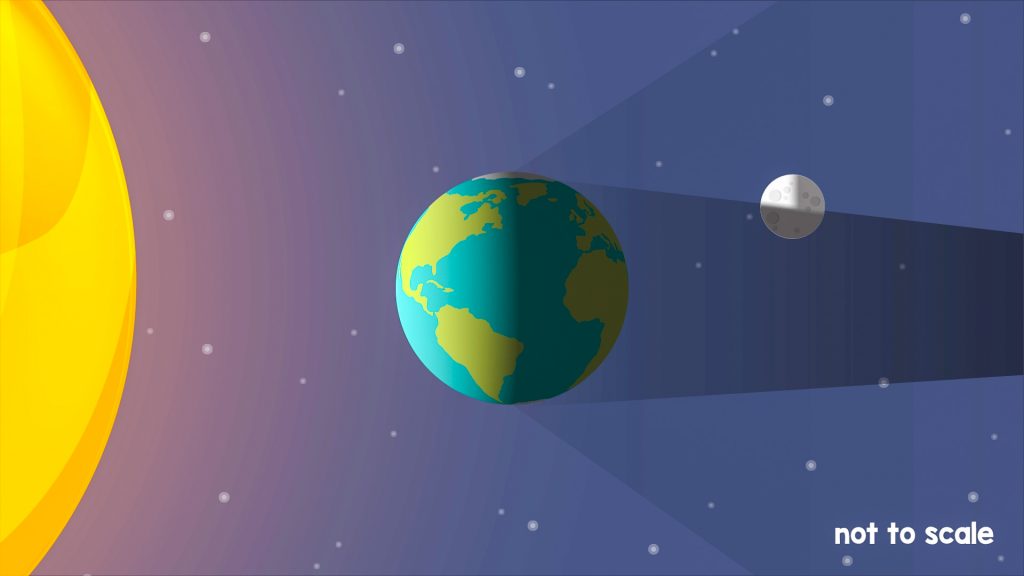
A solar eclipse occurs when the Sun, Earth, and Moon are in alignment and the Moon blocks light from the Sun, creating shadows on Earth. A lunar eclipse occurs when the Sun, Earth, and Moon are in alignment and Earth blocks light from the Sun, creating a shadow on the Moon.
To better understand solar & lunar eclipses…
LET’S BREAK IT DOWN!
Solar Eclipse

A solar eclipse happens when the Moon’s orbit causes it to move between Earth and the Sun. When this happens, the Moon casts a shadow over Earth. A solar eclipse can occur only at the phase of new moon, at which point the Moon cannot be seen because its lighted half is facing the Sun and its dark side faces Earth. Solar eclipses occur because the Moon is about 400 times closer to Earth than the Sun and about 400 times smaller. Those proportions, coupled with its elliptical orbit around the Earth, allow the objects in this Earth-Sun-Moon system to occasionally align in such a way that the Moon can appear to block the Sun. During a total solar eclipse, the Sun’s atmosphere, or corona, is visible.
Lunar Eclipse

Lunar eclipses happens when Earth blocks the Sun’s light from reaching the Moon. A lunar eclipse can occur only when the orbits of the Sun, Earth, and Moon are in complete alignment. Additionally, they can occur only when the Moon is full, meaning that you can see its entire surface with an unaided eye. There are three types of lunar eclipses: total, partial, and penumbral. The most dramatic of the three occurs during a total lunar eclipse, during which Earth’s shadow completely covers the Moon.
Blood Moon

A Blood Moon sometimes occurs during a total lunar eclipse. Lunar eclipses happen when the Earth moves between the Moon and the Sun. This casts a large shadow on the Moon, putting the Moon in darkness. Total lunar eclipses occur during the full moon phase of the Moon. This means the Sun, Earth, and Moon are in a line and in the same plane. Although Earth is casting a shadow on the Moon during a total lunar eclipse, we can still see the Moon because the Sun is still shining and beams of light bend around the Earth. When the sunlight passes through Earth’s atmosphere, some light becomes filtered and scattered. The longer light wavelengths pass through the atmosphere, whereas the shorter ones are scattered, causing the Moon to appear reddish from Earth.
Astronomers

Astronomy is one of the oldest fields of science and deals with the study of celestial objects, space, and the universe. Historically, astronomy focused on observations of heavenly bodies as ancient civilizations studied the night sky. Modern-day astronomers study the history of the solar system and investigate objects in space. There are many different kinds of astronomers and each study different parts of the universe. For example, planetary astronomers focus on growth, evolution, and death of planets, whereas solar astronomers spend their time analyzing a single star or sun.
Kepler Space Telescope

NASA designed the Kepler Space Telescope to be an observatory in space and launched it into orbit in 2009. The purpose of this project was to have a telescope dedicated to finding planets outside our solar system, with a particular focus on finding planets that might resemble Earth. Astronomers were able to discover more than 2,000 new planets and systems using the Kepler Space Telescope. The Kepler Space Telescope ran out of fuel in 2018, so it can no longer be used to make discoveries even though it is still orbiting in space.
SOLAR & LUNAR ECLIPSES VOCABULARY
SOLAR & LUNAR ECLIPSES DISCUSSION QUESTIONS
If the Sun is so much larger in size than the Moon, why do they appear to be the same size?
Why was it important that Dr. Jeff use a large ball to represent the Sun, a marble to represent Earth, and a bead to represent the Moon in his model?
How would the Earth-Sun-Moon system change if the Moon’s orbital plane weren’t tilted 5°?
What would happen during a total solar eclipse if you decreased the size of the Moon?
Is a solar eclipse the result of a cause-and-effect relationship? Be sure to include evidence to support this claim.
How are we able to predict when an eclipse may occur?
Skip, I will use a 3 day free trial
Enjoy your free 30 days trial
We use cookies to make your experience with this site better. By using this site you agree to our use of cookies. Click "Decline" to delete and block any non-essential cookies for this site on this specific property, device, and browser. Please read our privacy policy for more information on the cookies we use.Learn More
We use cookies to improve your experience. By using this site, you agree to our use of cookies. Click "Decline" to block non-essential cookies. See our privacy policy for details.Learn More






