Electromagnets are used in MRI machines. Electromagnets are commonly used in motors, speakers, and doorbells.

Forces can be applied at a distance through magnetism and static electricity. A magnet is an object that can attract some metals like iron. Static electricity can also attract objects without touching them, but it works a bit differently. It can attract and repel due to electrical charges.
To better understand magnets and static electricity…
LET’S BREAK IT DOWN!
All magnets produce a magnetic field.
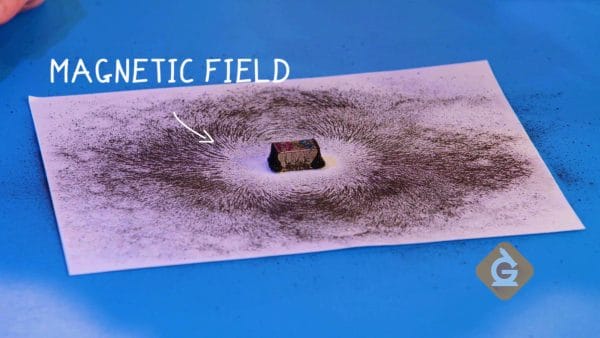
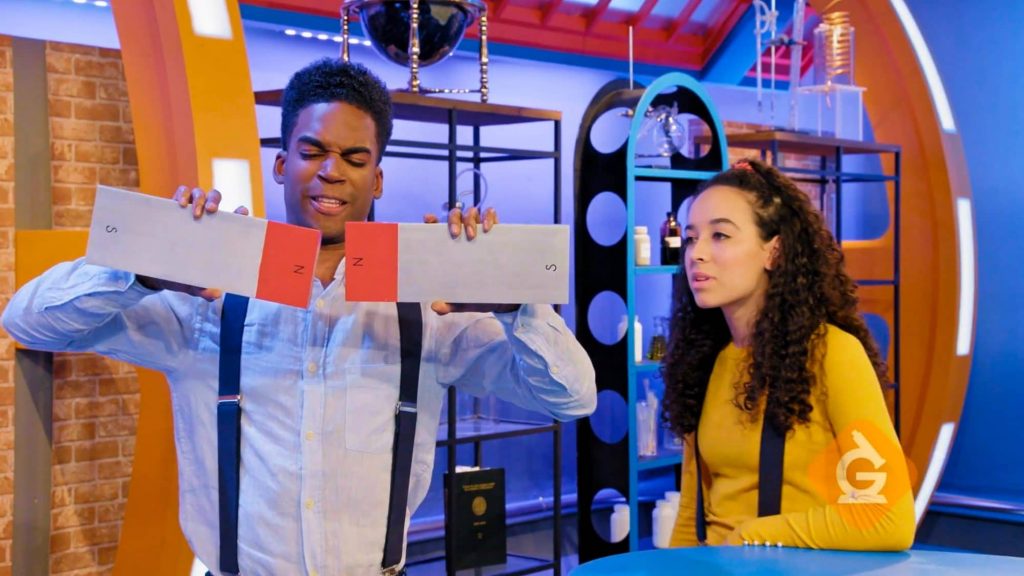
All magnets have a north and south pole. Magnetic poles are the strongest parts of a magnet.
North and south poles of magnets attract each other. The two south poles and the two north poles repel each other.
A magnetic field is the area around a magnet that attracts and repels objects. If you place an object inside the magnet’s field, it will be attracted to the magnet. The simplest way to see a magnetic field is to sprinkle iron filings around a magnet.
Iron filings are tiny pieces of iron. When sprinkled around a magnet, they reveal the magnetic field.
The Earth also has a magnetic field - it is like a huge magnet. Compasses work because the needle inside the compass is a magnet. One side of the needle is the north pole and the other side of the needle is the south pole. The north pole of the needle is attracted to the North Pole and the south pole of a needle is attracted to the South Pole.
The closer magnets are, the stronger the force.

Magnetism works over a distance. However, the closer the objects are to each other, the stronger the magnetic force. If you try to pull magnets apart it is very hard because the magnets are so close to each other. Once you get them a little bit apart it is much easier.
Electromagnets can be turned on or off with electricity.

An electromagnet is a magnet that uses electricity. The strength of an electromagnet can be changed by changing the amount of electricity that it is connected to.
By taking away the electricity running through the electromagnet, it can be turned off. In the video, Dr. Jeff used an electromagnet to pick up paper clips. When he pulled the wires off the battery, the paper clips fell off.
Electromagnets are used to power doorbells, construction cranes, and speakers.
Magnets called permanent magnets cannot be turned off. These magnets do not need electricity to work.
Static electricity can push or pull things without touching them.
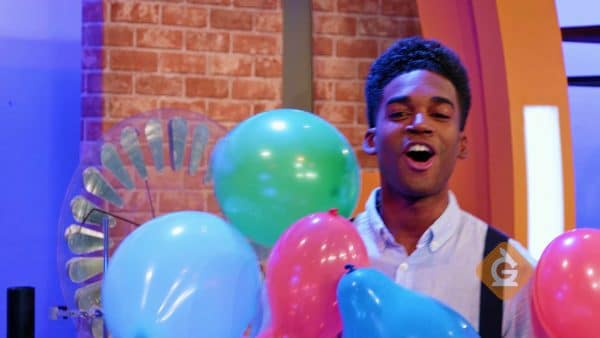
Static electricity is the buildup of the electrical charge in an object when it is rubbed against another object.
Static electricity causes objects to stick together when they have opposite charges and repel when they have the same charge.
Common examples of this include rubbing a party balloon on your head. Electrical charge is transferred between the balloon and your hair. They develop OPPOSITE charges which make the balloon be attracted to your hair.
Also, if you shuffle your feet across the carpet and then touch a doorknob, that is static electricity too. The charges were built up when your feet were rubbing on the carpet, and then the charge was transferred to the metal doorknob.
MAGNETS & STATIC ELECTRICITY EXAMPLES

Ferrofluid is a magnetic liquid. Ferrofluid is made of ultra tiny pieces of iron suspended in oil. It makes cool shapes when a magnet comes close to it.
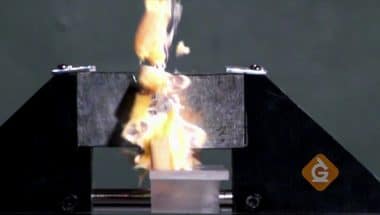
Neodymium magnets are a type of very strong permanent magnet. This magnet is so strong it can smash fruit. You must be very safe when handling large neodymium magnets.
MAGNETS & STATIC ELECTRICITY VOCABULARY
MAGNETS & STATIC ELECTRICITY DISCUSSION QUESTIONS
If magnetic fields are invisible, how do we know they are there?
Is an aluminum can magnetic or non-magnetic? Why or why not?
Why do the neodymium magnets come together and pulverize the fruit?
How are magnetic force and distance from an object related?
How can a nail become an electromagnet and magnetically attract paper clips?
Do the balloon and plastic bag used in the levitation device have the same or opposite charges?
How does the hair and Van de Graaff generator compare to what happens with magnets?
What are some problems that can be solved with magnets?
How does static electricity push and pull things from a distance?
Skip, I will use a 3 day free trial
Enjoy your free 30 days trial
We use cookies to make your experience with this site better. By using this site you agree to our use of cookies. Click "Decline" to delete and block any non-essential cookies for this site on this specific property, device, and browser. Please read our privacy policy for more information on the cookies we use.Learn More
We use cookies to improve your experience. By using this site, you agree to our use of cookies. Click "Decline" to block non-essential cookies. See our privacy policy for details.Learn More






