Convex mirrors allow us to see a wider view. This can help drivers see oncoming cars and drive more safely.
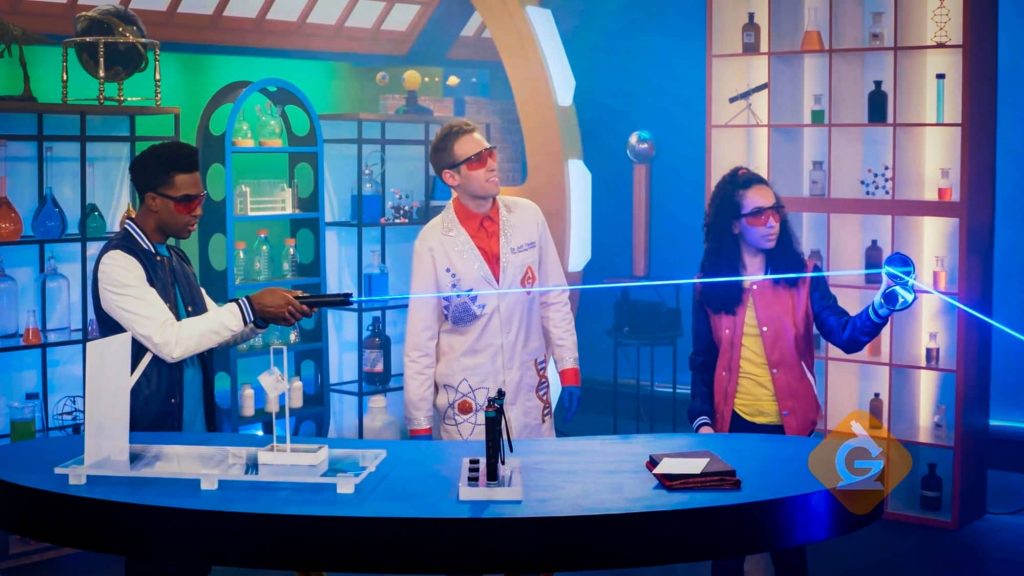

We can see because of light. Most light comes from the sun, light bulbs, and lasers. Light is a form of energy that moves in straight lines. It also reflects off things, and that reflected light enters our eyes, allowing us to see.
To better understand how light works….
LET’S BREAK IT DOWN!
There are many sources of light.

Sources of light can be divided into two groups: natural and made by humans. The sun is the most important natural source of light. The sun allows us to see during the day. Stars and lava from volcanoes also produce their own light. Some animals can produce their own light, such as fireflies and some glowing jellyfish.
Humans have created other sources of light. Light bulbs help us see in dark areas. Before light bulbs were invented, people used candles to provide light.
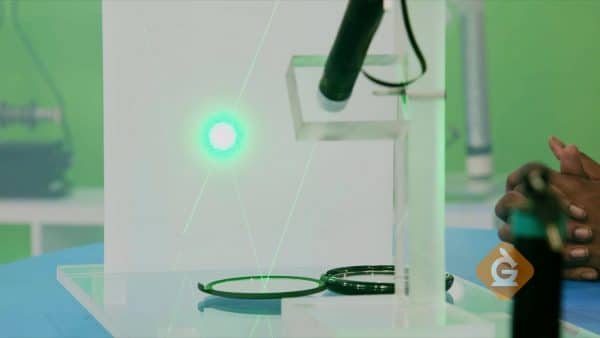
Laser beams are another source of light. Some high-powered laser beams can cause chemicals to explode!
Light travels in straight lines and reflects off things.

Light travels in a straight line from its source. It will keep moving in a straight line until it hits something.
If you have ever worn a hat on a sunny day, you have tested this idea. The brim of the hat blocks the sun from hitting our eyes.
Light reflects off objects and allows us to see. Some objects reflect light very well, like mirrors and white papers. Other objects, like brown construction paper, do not reflect as much light.
Water is also good at reflecting light off its surface. If you have ever been near a pool on a sunny day, your eyes may have hurt from too much light reflected from the water. Hats help block sunlight, but not the light that is reflected off the surface of water.
Light reflects off things and enters our eyes.
We see objects because they either give off their own light, or light reflects off the objects and enters our eyes.
The moon is an interesting example. It doesn’t make its own light - we can see the moon because it reflects light from the sun.
If an object did not reflect any light, we would not be able to see it.
Our eyes do not produce light, they detect it.

Our eyes are amazing and allow us to detect light, focus on images, and see what is around us. The lens of the eye helps make images easier to see by focusing light. There are many other parts of the eye that work together to help you see. Some parts allow you to see color, and other parts detect the shapes of objects.
After the eye collects information about what you are seeing, it quickly sends the information to the brain. Believe it or not, the images that our eyes send to the brain are upside-down! Our brain flips it. The brain also tries to make sense of what we are seeing.
LIGHT REFLECTION AND VISION EXAMPLES


CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray Discs use the science of reflection. Inside a blu-ray player is a laser which reflects light off the disk. This allows the blu-ray player to read the information on the disk.

Fiber optic cables transmit signals very quickly. They are frequently used to transmit information over the internet.
LIGHT REFLECTION AND VISION VOCABULARY
LIGHT REFLECTION AND VISION DISCUSSION QUESTIONS
Why does fog help us see laser beams?
Why is the image the camera obscura produces upside down?
If the image produced by the camera obscura is not in focus, what can be done to focus it?
Are other materials, besides a mirror, reflective? How do you know?
How do CDs, DVDs and Blu-Ray discs use light reflection to work?
Skip, I will use a 3 day free trial
Enjoy your free 30 days trial
We use cookies to make your experience with this site better. By using this site you agree to our use of cookies. Click "Decline" to delete and block any non-essential cookies for this site on this specific property, device, and browser. Please read our privacy policy for more information on the cookies we use.Learn More
We use cookies to improve your experience. By using this site, you agree to our use of cookies. Click "Decline" to block non-essential cookies. See our privacy policy for details.Learn More






