You will learn what area is, how area is measured, how to find area by counting square units, and how to find the area of rectangles using addition or multiplication. You will also learn that area is additive and shapes can be composed and decomposed to find the area of shapes formed by rectangles.
To better understand finding area…
LET’S BREAK IT DOWN!
Somersaults

Area is measured in square units. Let’s say you want to make a floor mat for a tumbling class. You put 5 rows that each have 2 square pads. You can count the number of squares to find the area you can tumble on and find that the area is 10 square units. Try this one yourself: You lay 24 square pads in a rectangular mat for a wrestling class. Then, you pick up 4 of the pads. What is the area of the new mat?
Defenders of the Area

Different shapes can have the same area, as long as the same number of square units are needed to fill the space. You can also add or remove square units for a larger or smaller area. Let’s say you have a cape that is made of 27 squares of fabric of the same size. It is 9 squares long and 3 squares wide. You remove 6 squares from the bottom of the cape and attach them to a side to use as a hood. The area of your cape is still 27 square units. Try this one yourself: You use 12 square units of fabric to make a cape that is 3 squares long and 4 squares wide. Your cape is not long enough, so you add 9 more squares at the bottom. What is the area of your cape now?
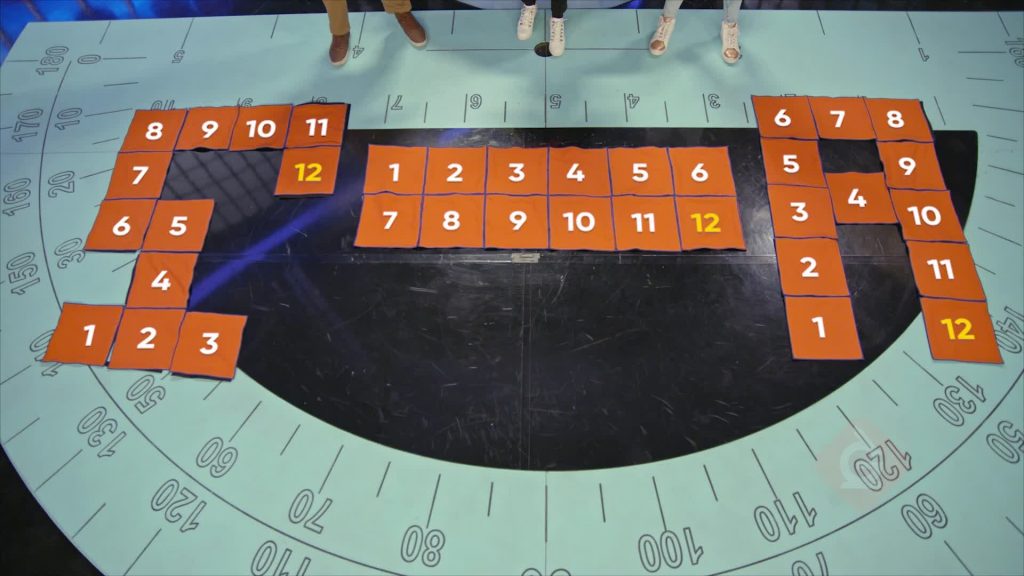
Poster Array

The area of a rectangle or square can be thought of as an array, with rows and columns of square units. To find the number of square units in the shape, you can multiply the number of columns by the number of rows. This is the same as multiplying the length by the width. Let’s say you have square posters that you are using to cover a wall. The wall fits 5 posters high and 5 posters wide. You can multiply 5 times 5 to find that the total area of the wall is 25 square posters. Try this one yourself: One-foot square posters are used to cover a wall. The wall is 6 posters high and 4 posters wide. What is the area covered by the posters?
Pixel Art
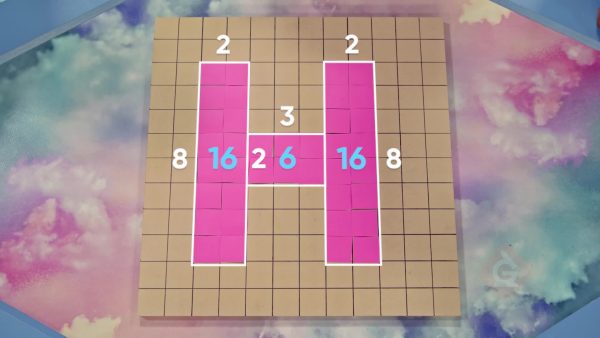
Shapes are not always perfect squares or rectangles. Sometimes you can break shapes apart into squares and rectangles to find their area. Let’s say you have a T-shaped figure that can be broken into a 2 × 2 square and a 6 × 2 rectangle. You can multiply to find that the area of the square is 4 square units and the area of the rectangle is 12 square units. Then, you can add the two areas to find that the area of the full shape is 4 + 12 = 16 square units. Try this one yourself: You have a U-shaped figure that can be broken into 2 rectangles that are 6 units long and 3 units wide and one square with a side length of 3 units. What is the area of the figure?
INTRO TO FINDING AREA VOCABULARY
INTRO TO FINDING AREA DISCUSSION QUESTIONS
What is area? How is it measured?
How could you find area using grid paper?
How can an array help you find the area of a rectangle that is 6 inches long and 8 inches wide?
How can you find the area of a shape that is not a square or rectangle, such as an L-shape or T-shape?
Garrett puts square photos in a shape that is 8 photos wide and 10 photos tall. Lars takes the same photos and puts them in a shape that is 12 photos wide and 5 photos tall. How many of the photos does Lars have left over? Explain how you know.
Skip, I will use a 3 day free trial
Enjoy your free 30 days trial
We use cookies to make your experience with this site better. By using this site you agree to our use of cookies. Click "Decline" to delete and block any non-essential cookies for this site on this specific property, device, and browser. Please read our privacy policy for more information on the cookies we use.Learn More
We use cookies to improve your experience. By using this site, you agree to our use of cookies. Click "Decline" to block non-essential cookies. See our privacy policy for details.Learn More






