Cells are the basic unit of all living things. All cells need energy, get rid of waste and contain genetic material to make more cells. Some living things are made of only 1 cell (unicellular) and other organisms like humans are made of many cells working together (multicellular).
To better understand cells…
LET’S BREAK IT DOWN!
All living things are made of cells.
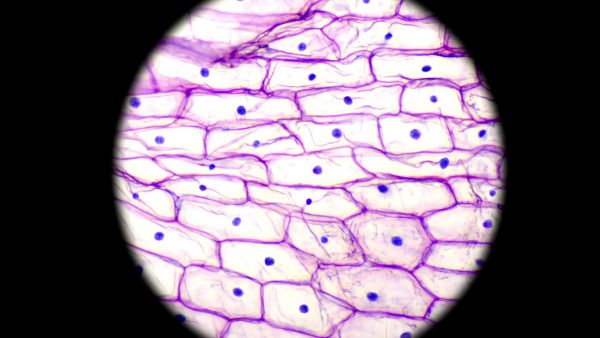
Cells can be seen with a light microscope which can magnify objects up to 1,000 times. Typically a microscope slide is prepared which creates a thin layer of cells and holds them in place. Dye is used to stain the cells, making them easier to see. Cells can range in size. For example, an amoeba is about 1 mm in length and the biggest ones can be seen without a microscope. A red blood cell is 100x smaller at 0.01 mm and a bacteria is 1000x smaller than an amoeba at about 0.001 mm.
Plant & Animal Cells Have Organelles.
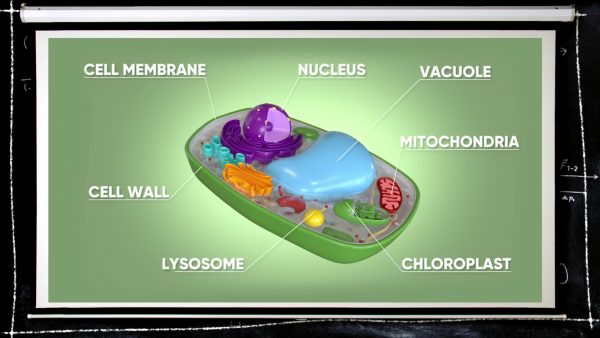
Organelles are parts of a cell that help the cell to function and stay organized. The mitochondria, for example, is where sugars are used to produce energy. The vacuole is a membrane bound organelle that stores fluids. The cell membrane controls what comes in and out of a cell. Plant and animal cells need organelles in order to carry out their everyday functions.
Cells are specialized, depending on their function.
Not all cells are the same. In the human body, for example, there are many kinds of cells. A nerve cell has long arm like features to help the cell communicate with other nerve cells. A muscle cell is more tubular in shape and it can get longer and shorter when muscles contract. These kinds of differences between the cells of an organism is called cell differentiation. Cells are structured in ways that help them achieve their function.
Plant and animal cells have similarities and differences.
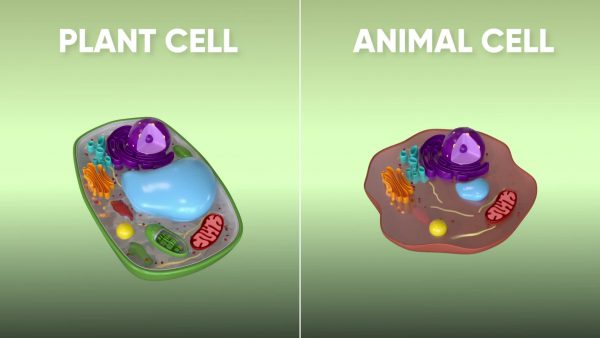
Although plant and animal cells have many of the same organelles, there are some notable differences. Plant and animal cells both have a cell membrane, but in addition to a cell membrane, a plant cell also has a cell wall. The cell wall gives the plant cell structure. Plant cells also contain chloroplasts, green organelles that do photosynthesis. Animal cells do not have chloroplast because they do not do photosynthesis.
Studying cells can help us cure diseases.

There are several specialized types of scientists that study cells. Pathologists look at human cells under microscopes to diagnose diseases. For example, red blood cells normally have a disc like shape. In a disease called sickle cell anemia, cells are shaped like the letter “c” and this can be seen under a microscope to diagnose the disease so the patient can get treatment. Many other types of scientists also study cells such as molecular biologists, biochemists and more.

































































































































 Select a Google Form
Select a Google Form









